Details
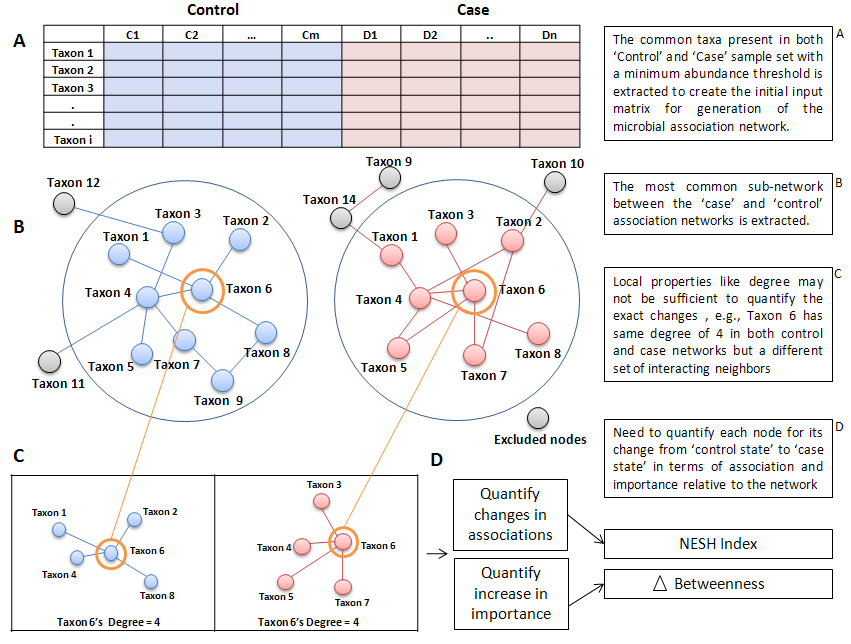
The combined effect of mutual associations within the co-inhabiting microbes in human body is known to play a major role in determining our health status. The differential taxonomic abundance between a healthy and disease state are often used to identify microbial markers. However, in order to make a microbial community based inference, it is important not only to consider microbial abundances, but also quantify the changes observed among inter microbial associations. We introduce a method called ‘NetShift’ to visualize community shufflings in microbial association networks between healthy and diseased states and identify 'driver' nodes observed between the states. The ‘NetShift’ web server allows easy visual analysis of ‘case’ and ‘control’ microbial association networks requiring users to simply upload the corresponding networks as edge lists. All results are presented as user friendly and interactive charts/tables allowing easy biological inferences. A summary of the algorithm is shown in the figures below.
Algorithm